sodium silicate production line, commonly known as water glass, is a versatile compound used in various industries, including construction, detergents, and food processing. Its production technology has evolved significantly over the years, driven by advancements in chemical engineering and increasing demand for sustainable practices. This article explores the future trends and developments in sodium silicate production technology.
Current Production Methods
The traditional methods of sodium silicate production involve the reaction of silica sand with sodium carbonate at high temperatures. This process, while effective, is energy-intensive and has a significant environmental impact. As industries seek to reduce their carbon footprint, there is a growing interest in more sustainable production methods that minimize energy consumption and waste generation.
Emerging Technologies
Recent advancements in production technologies are paving the way for more efficient methods of sodium silicate synthesis. One notable development is the use of alternative raw materials, such as rice husk ash and other agricultural by-products. These materials not only reduce reliance on traditional silica sources but also contribute to waste management efforts in the agricultural sector.
Green Chemistry Initiatives
The principles of green chemistry are becoming increasingly relevant in sodium silicate production. Manufacturers are exploring ways to reduce hazardous substances and improve the overall sustainability of their processes. This includes the use of non-toxic solvents and catalysts, as well as the implementation of closed-loop systems that recycle waste materials back into the production cycle.
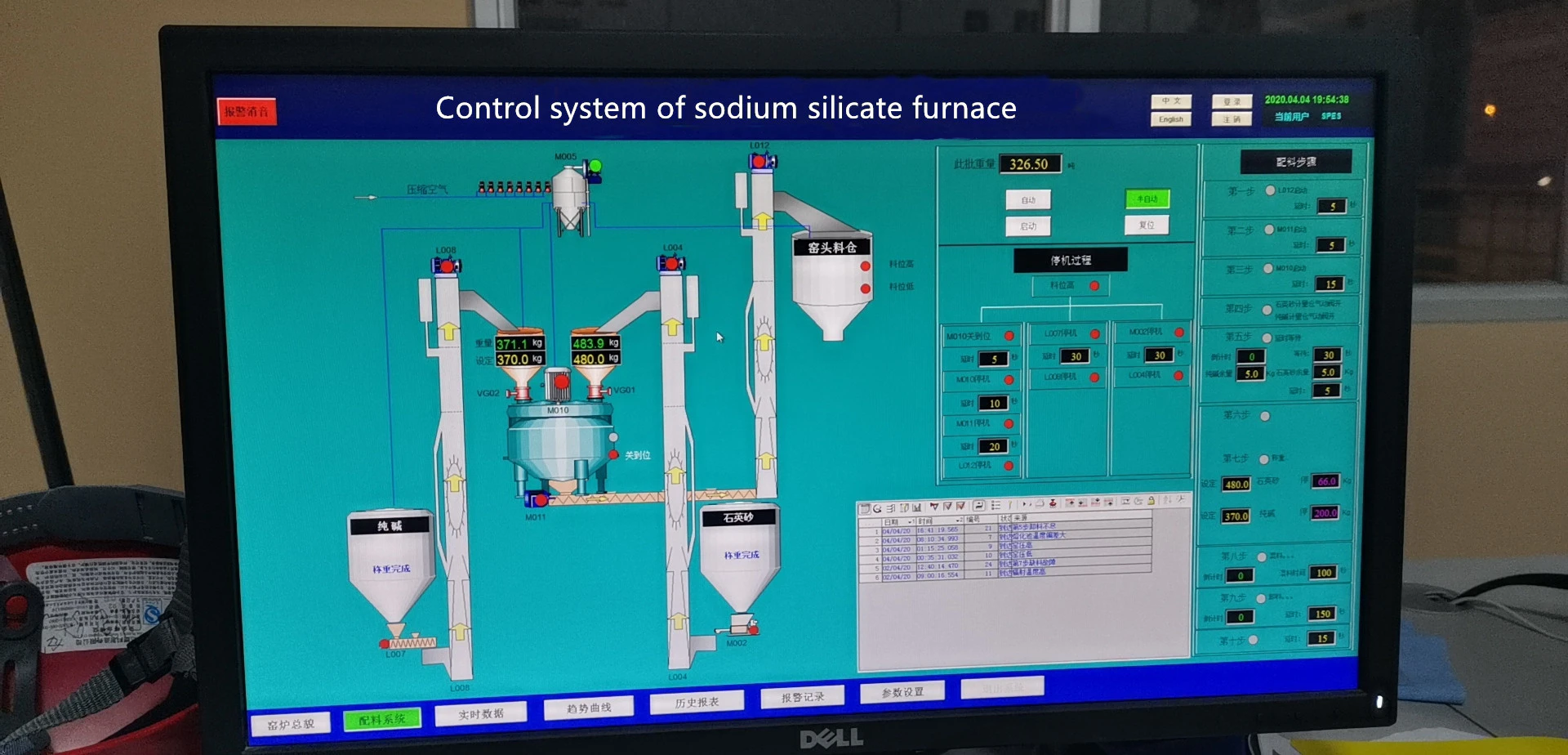
Automation and Industry 4.0
The integration of automation and Industry 4.0 technologies is transforming sodium silicate production. Smart manufacturing techniques, including the Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence (AI), enable real-time monitoring and optimization of production processes These technologies enhance efficiency, reduce downtime, and improve product quality, making them essential for future developments in the industry.
Energy Efficiency Improvements
Energy efficiency is a critical concern in the production of sodium silicate. Future trends indicate a shift towards the use of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, to reduce the carbon footprint of production facilities. Additionally, advancements in heat recovery systems can capture and reuse energy generated during production, further enhancing overall efficiency.
Market Demand and Applications
The demand for sodium silicate is expected to grow in various sectors, including construction, automotive, and electronics. As industries evolve, new applications for sodium silicate are emerging, such as its use in advanced materials and nanotechnology. This growing market demand will drive innovation in production technologies to meet the specific needs of these applications.
Regulatory Considerations
As environmental regulations become more stringent, sodium silicate producers must adapt their practices to comply with new standards. This includes reducing emissions, managing waste, and ensuring the safety of chemical processes. Companies that proactively embrace regulatory changes will not only enhance their reputation but also gain a competitive advantage in the market.
Research and Development Efforts
Ongoing research and development efforts are crucial for advancing sodium silicate production technology. Collaboration between academia and industry can lead to innovative solutions that address current challenges. Investment in R&D will facilitate the discovery of new production methods and the optimization of existing processes, ensuring the long-term sustainability of the industry.
Global Perspectives
The production of sodium silicate is a global endeavor, with key players located in various regions. Understanding regional differences in production practices, regulations, and market demands is essential for companies looking to expand their operations internationally. Global collaboration and knowledge sharing will play a vital role in shaping the future of sodium silicate production technology.
Conclusion
The future of sodium silicate production technology is poised for significant advancements driven by sustainability, efficiency, and innovation. As industries continue to evolve, the demand for more environmentally friendly production methods will shape the development of new technologies. By embracing these trends, sodium silicate producers can position themselves for success in a rapidly changing market.








