Printed Circuit Board Basics
Most of us are using Printed Circuit Board in our daily life. Printed Circuit Boards are used in almost all the Electronic products, from consumer gadgets such as PCs, tablets, smartphones, and gaming consoles to industrial and even high tech products in strategic and medical electronics domains.
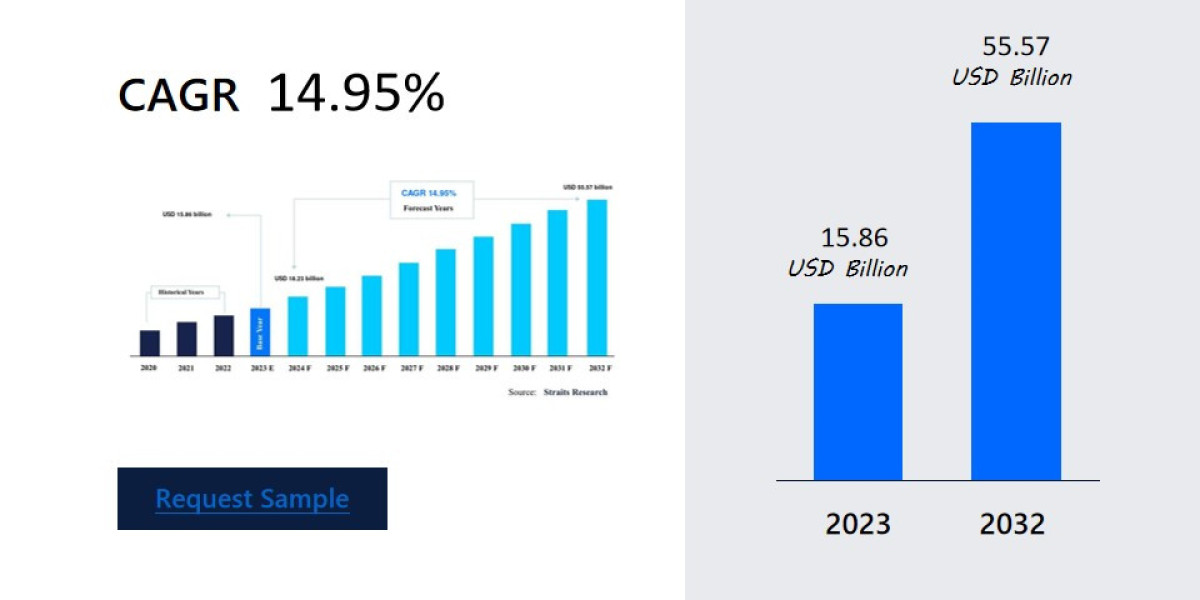
Here, we have some statistics for you that shows how many electronic devices connect worldwide from 2015 to 2025. This statistic shows an increase in the use of a number of PCB in people's daily life. Hence, CircuitWala took this opportunity to provide a basic knowledge about PCB via this article.
There are so many books available online which teach about Printed Circuit Board design and hardware parts. There are few links available online which show only a few basic fundamentals of PCB and few are there for Basics of Printed Circuit Board (PCB) Design. Few which gives good knowledge on Printed Circuit Board terminology. But in the end for the hobbyist, there is no such material available which makes their work easy.
Nowadays there are few online designing websites available which allow hobbyists and students to create their design and Printed Circuit Board fabrication part. These websites provide limited features and charge high for the full edition. We, @CircuitWala are trying to provide one platform which provides plenty of Printed Circuit Board knowledge digitally to make your work simple and easy.
Alternatives of PCB include wire wrap and point-to-point construction. Creating a layout of PCB is a little bit time-consuming method as compared to its alternative solution but manufacturing of PCB is cheaper and faster then other wiring methods as electronic components are mounted and wired with one single part.
Let’s start with some basics of Printed Circuit Board with this article. Here in this article we will discuss about history of PCB to understand the emerge of PCB, Types of PCB to make your complex PCB a very simple using different types, Usage of PCB to provide you an idea to create more Printed Circuit Board projects, Advantages and Disadvantages, Possible Future to know about new technological change in Printed Circuit Board manufacturing and also about how to destroy and manage your PCB’s e-waste? We know you are eager to know all the stuff in detail but before that let’s make a simple definition of Printed Circuit Board.
What is a Printed Circuit Board?
Printed Circuit Board is an electronic device made of conductive material(FR-4) like copper which connects components mounted on it to get desired output by providing an input on another end.
When the board has not mounted any of the components is called a Printed Circuit Board or Printed Wire Board. Mounting of an electronic component on a Printed Circuit Board is called PCB assembly.
History of Printed Circuit Board
The invention of the Printed Circuit Board was by Austrian engineer Paul Eisler as part of a radio set while working in England around 1936.
In the early days before Printed Circuit Board became common in use, Point-to-Point construction was used. This meant some bulky and unreliable design that required plenty of sockets and regular replacement of it. Most of this issue was directly addressed when PCB went into regular production.
Originally, every electronic component had wire leads, and the PCB had holes drilled for each wire of each component. The components’ leads were then passed through the holes and soldered to the PCB trace. This method of assembly is called Through-Hole construction. There is one other method to mount components called Surface Mount.
Type of Printed Circuit Board
PCBs are produced from the different types of material and on the basis of that material PCBs are divided mainly into two parts: Rigid PCB and Flexible PCB. Nowadays, a combination of Rigid and flexible PCB is also possible and that is called Flexi-Rigid PCBs.
Most of the PCBs are built in layers. The inner layer is the base material called a substrate. Rigid PCBs are mainly made of material like epoxy materials and Flexible PCBs are made of plastic material that can withstand high temperatures.
Rigid PCBs are generally hard materials that hold the component in a better way. The motherboard in the tower of a computer is the best example of Rigid PCBs. Flexible PCBs fundamental material allows PCBs to fit into forms that Rigid PCBs can not. Flexible PCBs can turn round without harming the circuit on the PCB.
All Rigid and Flexible PCBs can come in three formats by layers: Single Layer, Double Layer, and Multi-Layer.
1. Single Layer PCB
Single Layer PCBs have been around since the late 1950s and still dominate the world market in sheer piece volume. Single Sided PCBs contain only one layer of conductive material and are best suited for low-density designs. Single-sided PCBs are easy to design and quick to manufacture. They serve as the most lucrative platform in the industry.
2. Double Layer PCB
Double Layered printed circuit board technology is conceivably the most popular type of PCB in the industry. Double Sided PCB (also known as Double-Sided Plated Thru or DSPT) circuits are the gateway to advanced technology applications. They allow for a closer (and perhaps more) routing trace by alternating between top and bottom layers using vias.
3. Multi Layer PCB
Multilayer PCB is a circuit board that has more than two layers. Unlike a Double-Sided PCB which only has two conductive layers of material, all multilayer PCBs must have at least three layers of conductive material which are buried in the center of the material.
Usage of Printed Circuit Board
By reading this article till this point, we hope that you are now able to get about printed circuit boards. Now, we will make you understand about different applications of printed Circuit Board.
In this digital world, Printed Circuit Board is in almost all our daily life electronic devices and in our industrial electronics as well. Below are the industries where PCBs are used:
Possible Future
Nowadays, most of the circuits are replaced to produce Printed Circuit Board from the old methods. Revolution in technology made many of the processes automated and hence it is easy to manufacture PCB. But still, these processes are a bit expensive to hire, involve toxic waste and use high temperatures and acids. With technological advances we have seen in the past years, it is not hard to imagine PCB will soon be revolutionized. Not only that but research institutes predict a more ‘green’ future for PCBs; PCBs being made of paper.
Electronic Waste (e-waste)
Electronic Waste or e-waste is described as discarded electrical or electronic devices. Informal processing of e-waste in developing countries can lead to adverse human health effects and environmental pollution.
Electronic scrap components contain a hazardous substance such as lead, cadmium, beryllium, or brominated flame retardants. Recycling and disposal of e-waste may involve significant risk to health of workers and communities in developed countries and great care must be taken to avoid unsafe exposure in recycling operations
Nowadays, developing countries are encouraging electronic users to take care while recycling the e-waste or submit them to the organization who are involved in such activities.
Summary
In this blog, we have learned the basics of Printed Circuit Board. CircuitWala is planning to write as many blogs to provide more and more knowledge of Printed Circuit Board. Either it is basics or manufacturing or usages or advantages and disadvantages of PCBs. We will also try to make our users/customers up to date for the new technology innovations, including past histories and revolution of the PCB industries.
In the next blog, we will look at more briefly about the different types of Printed Circuit Board. We also understand the process to make it and different usage and application for the same.