The global solar inverter market growth is poised for dynamic growth over the next decade, driven by the surging demand for renewable energy, enhanced government support, and ongoing technological innovations. As solar power becomes a cornerstone of the global energy mix, solar inverters are emerging as a critical component of photovoltaic (PV) systems, facilitating the smooth conversion of solar energy into usable electricity.
Download Sample Pages: https://www.snsinsider.com/sample-request/1343
Market Overview
Solar inverters serve a pivotal role in PV systems, transforming direct current (DC) from solar panels into alternating current (AC), which can power homes, businesses, and feed back into the electrical grid. With growing concerns about climate change, many countries are pushing for renewable energy integration, leading to a boom in solar installations across residential, commercial, industrial, and utility sectors.
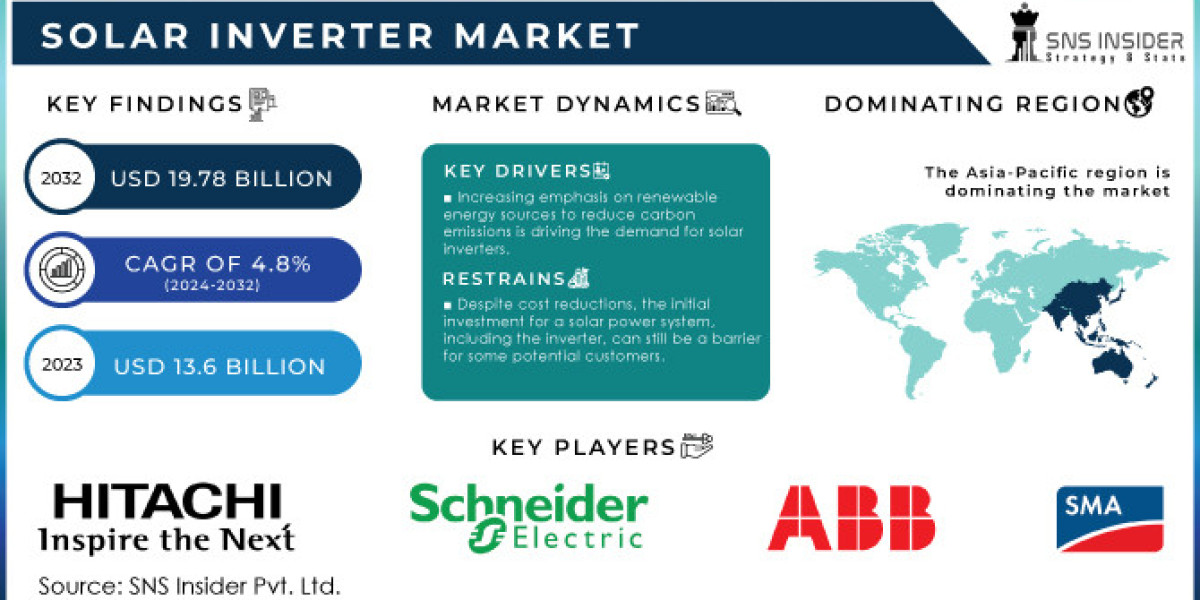
In 2023, the global solar inverter market was valued at USD 12.9 billion, and it is anticipated to surpass USD 47.44 billion by 2032, registering a CAGR of 18.5%. This impressive growth is underpinned by a combination of increased solar capacity, improved inverter technologies, and supportive energy policies worldwide.
Emerging Market Trends
Several key trends are shaping the growth trajectory of the solar inverter market:
Surge in Solar Energy Installations: With renewable energy at the forefront of global climate strategies, investments in solar power are skyrocketing. From small-scale residential installations to massive utility-scale solar farms, the demand for reliable, efficient inverters is expanding across all sectors.
Technological Innovations: New developments in inverter technology, including smart inverters, hybrid models with integrated battery storage, and remote monitoring capabilities, are boosting system performance and energy efficiency. This has made solar power more accessible and affordable for both consumers and businesses.
Energy Storage Integration: The integration of solar inverters with energy storage systems is gaining momentum. Hybrid inverters, which enable seamless energy storage and grid interaction, are becoming increasingly popular as they allow users to store excess solar power for later use, maximizing energy self-sufficiency.
Government Incentives and Policy Support: Many countries have implemented financial incentives, tax rebates, and subsidies to encourage the adoption of solar energy. Programs such as feed-in tariffs, net metering, and the Investment Tax Credit (ITC) in the U.S. are spurring growth in both residential and utility-scale solar projects, bolstering demand for solar inverters.
Decentralized Power Generation: As more homes and businesses adopt decentralized power systems, solar inverters are playing an essential role in facilitating grid independence. The growing trend of rooftop solar installations is fueling demand for smaller inverters that offer higher efficiency and flexibility.
Buy Now: https://www.snsinsider.com/checkout/1343
Market Segmentation
The global solar inverter market is segmented by type, product, application, and connectivity, each offering distinct advantages depending on the installation scale and energy requirements.
By Type
Central Inverters: Central inverters are designed for large solar power plants or utility-scale installations. They provide cost-effective solutions for managing high-volume solar energy, making them essential for large-scale renewable projects.
String Inverters: Ideal for residential and commercial applications, string inverters are widely used in medium-sized solar installations. They offer excellent scalability and flexibility, allowing for easy maintenance and lower operational costs.
Micro Inverters: Popular in rooftop solar systems, micro inverters convert power at the panel level, increasing overall system efficiency and providing better performance, especially in shaded areas. They also offer real-time monitoring at the individual panel level, which is beneficial for maximizing energy production.
Hybrid Inverters: These inverters combine solar power generation with energy storage capabilities, making them ideal for installations that include batteries. Hybrid inverters support energy management by storing excess power and providing backup during outages or peak demand periods.
By Product
On-grid Inverters: Also known as grid-tied inverters, these are connected to the main electricity grid and allow for the export of excess solar energy back into the grid. On-grid inverters are widely used in urban areas with stable grid infrastructure.
Off-grid Inverters: Off-grid inverters are used in isolated systems where no connection to the main grid exists, often in remote or rural areas. They are crucial for standalone power systems that rely on solar energy to meet all energy needs.
Hybrid Inverters: These inverters are gaining traction due to their ability to manage both solar power generation and energy storage. They provide flexibility for users who want to utilize battery systems to store and use solar energy when needed.
By Application
Residential: The residential sector is experiencing a strong uptick in solar inverter demand, driven by increased rooftop solar installations. Homeowners are adopting solar inverters to reduce electricity bills, enhance energy efficiency, and achieve greater energy independence.
Commercial & Industrial: Businesses and industries are adopting solar inverters as part of their corporate sustainability efforts. Inverters for commercial applications are designed to handle higher power outputs, making them suitable for factories, shopping centers, and office buildings.
Utilities: Utility-scale solar farms, which generate large amounts of energy to feed into the grid, rely on central inverters for their high capacity and efficiency. These large installations are key to meeting the growing demand for renewable energy.
By Connectivity
On-grid: On-grid solar inverters remain the dominant type, as they provide seamless integration with national grids and allow consumers to sell excess energy back to the grid under net metering programs.
Off-grid: Off-grid inverters are essential in areas with limited or no access to the main power grid. These systems, often paired with energy storage, offer users independence from grid electricity.
Regional Analysis
The solar inverter market is witnessing significant growth across various regions, with unique drivers shaping each market.
North America: The North American market, led by the U.S., continues to see rapid solar adoption, thanks to government incentives like the Investment Tax Credit (ITC) and state-level policies promoting renewable energy. The region’s well-established solar infrastructure and continued investment in energy storage technologies further drive the solar inverter market.
Europe: Europe is a leading region for renewable energy adoption, with countries like Germany, Spain, and the UK pushing for aggressive climate goals. The region’s focus on reducing greenhouse gas emissions, along with supportive policies such as feed-in tariffs, is fueling the demand for both residential and utility-scale solar inverters.
Asia-Pacific: The Asia-Pacific region is the fastest-growing market for solar inverters, driven by the rapid expansion of solar installations in countries like China, India, and Japan. Government programs promoting clean energy and a shift towards renewable power generation are key growth factors in this region.
Rest of the World: Emerging markets in Latin America and the Middle East & Africa are showing increased interest in solar energy as they seek sustainable energy solutions to meet rising demand and reduce reliance on fossil fuels. Solar inverters in these regions are gaining traction as cost-effective, scalable solutions for energy generation.