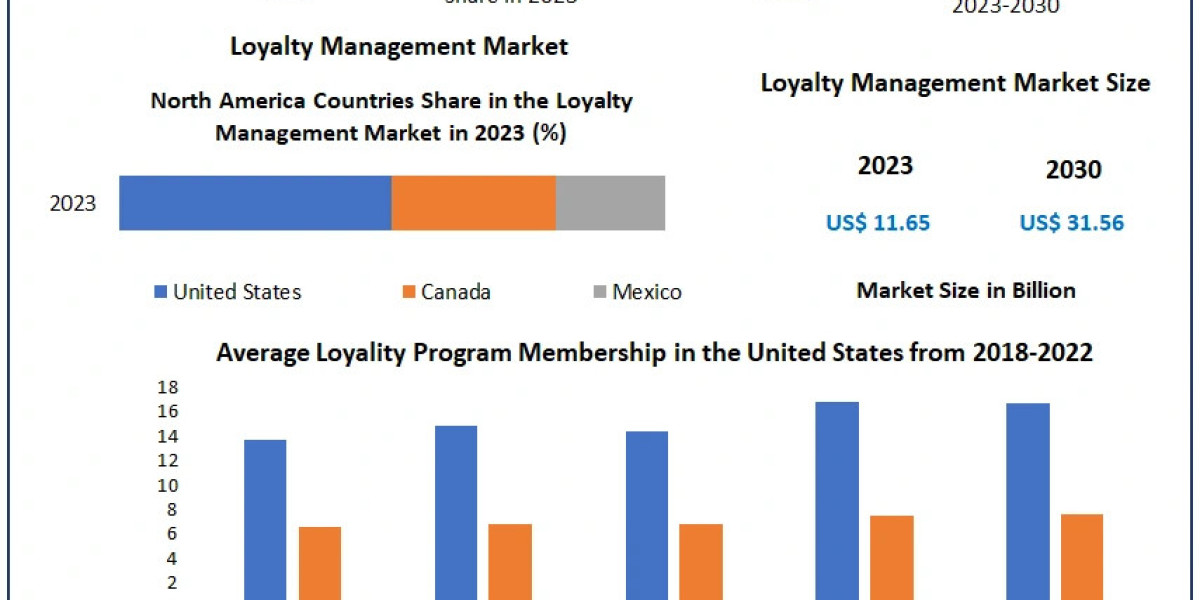
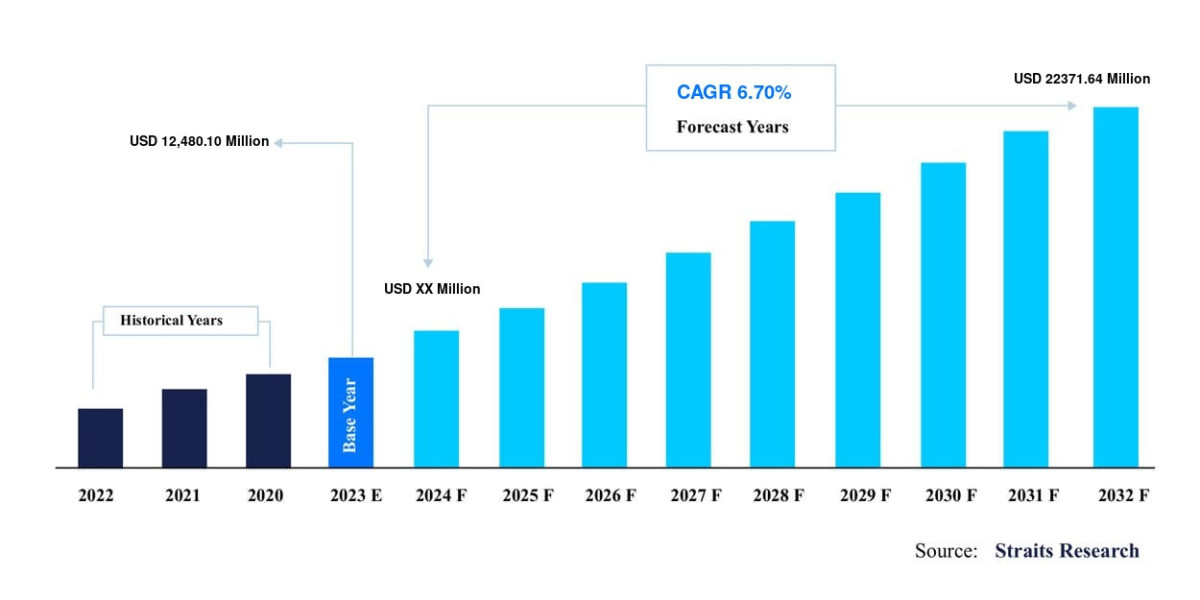
Plasmid preparation is a cornerstone technique in molecular biology that allows scientists to isolate and purify plasmid DNA from bacterial cells. Plasmids, small circular DNA molecules, are widely used in research for gene cloning, expression studies, and genetic engineering. Preparing high-quality plasmid DNA is essential for ensuring the success of downstream applications like sequencing, polymerase chain reactions (PCR), and transformation.
What Is Plasmid Preparation?
Plasmid preparation refers to the process of extracting and purifying plasmid DNA from bacterial cultures. The method separates the plasmid DNA from chromosomal DNA, proteins, and other cellular components. By following specific protocols, researchers can obtain a clean, concentrated plasmid sample suitable for experimental use.
Steps Involved in Plasmid Preparation
There are different types of plasmid preparation protocols, including mini, midi, and maxi preps, which vary based on the volume of bacterial culture used and the amount of DNA obtained. Here’s an outline of the most common method, the alkaline lysis protocol:
Bacterial Culture Growth
Begin by growing bacterial cells containing the plasmid of interest in a liquid culture medium with antibiotics. The antibiotics ensure that only cells carrying the plasmid survive and grow.Harvesting the Cells
The bacterial culture is centrifuged to pellet the cells at the bottom of the tube. The supernatant is discarded, leaving the bacterial pellet, which contains the plasmids.Cell Lysis
The cells are lysed using an alkaline solution containing sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and detergent (SDS). This step disrupts the bacterial cell wall and membrane, releasing the cellular contents, including plasmid DNA.Neutralization
A neutralization buffer is added to precipitate chromosomal DNA and proteins while leaving the plasmid DNA in solution. This forms a cloudy mixture, which is clarified by centrifugation.Plasmid Purification
The plasmid DNA in the supernatant is further purified using methods like ethanol precipitation or silica column-based purification. Modern kits simplify this step, allowing efficient recovery of plasmid DNA.Quantification and Quality Check
The purified plasmid DNA is quantified using spectrophotometry (e.g., at 260/280 nm) and checked for quality via agarose gel electrophoresis.
Applications of Plasmid Preparation
Plasmid preparation is essential for many scientific applications, including:
- Cloning and Genetic Engineering: Inserting plasmids into host organisms to study gene function.
- Gene Expression Studies: Using plasmids to express proteins in bacterial, yeast, or mammalian systems.
- Therapeutic Research: Developing plasmid-based vaccines or gene therapy vectors.
- Sequencing and Bioinformatics: Analyzing plasmid DNA for sequence verification or modification.
Tips for Successful Plasmid Preparation
- Use Fresh Cultures: Ensure bacterial cultures are fresh and healthy for optimal yield.
- Avoid Overgrowth: Overgrown cultures can lead to cell death and lower plasmid yields.
- Handle Gently: Avoid vigorous mixing during lysis and neutralization to prevent shearing of chromosomal DNA, which can contaminate the plasmid sample.
- Choose the Right Kit: Use a plasmid prep kit suited for your experimental needs (e.g., low-copy vs. high-copy plasmids).
Conclusion
Plasmid preparation is a critical step in molecular biology workflows, enabling researchers to isolate and study DNA with precision. With advances in technology, modern plasmid prep kits have made the process faster, more efficient, and highly reproducible. Mastering this technique is essential for any scientist working in the fields of genetics, biochemistry, or biotechnology. Whether you’re cloning genes or producing recombinant proteins, a high-quality plasmid preparation sets the stage for success.