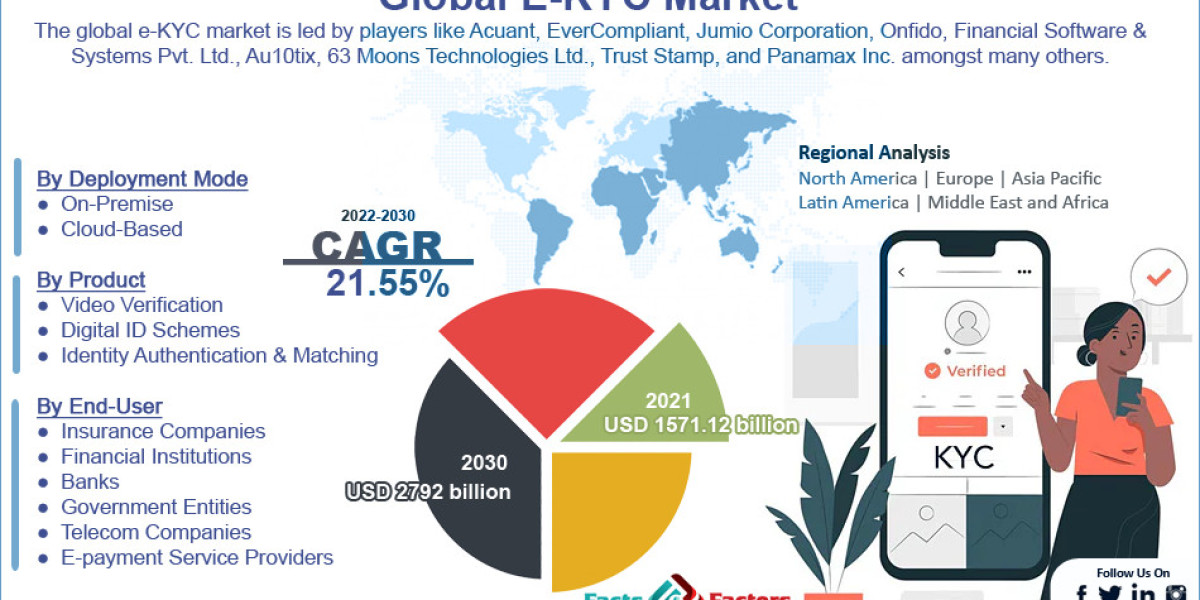
Levofloxacin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic belonging to the fluoroquinolone class. It is widely used to treat a variety of bacterial infections due to its effectiveness against both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria.
Key Information About Levofloxacin
Mechanism of Action
Levofloxacin works by inhibiting bacterial DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV, enzymes critical for DNA replication and repair. By disrupting these processes, levofloxacin prevents bacteria from reproducing and ultimately leads to their death.
Common Uses
Levofloxacin is prescribed for various infections, including:
- Respiratory Infections: Such as pneumonia and chronic bronchitis exacerbations.
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): Effective against complicated and uncomplicated UTIs.
- Skin Infections: Treatment for certain types of bacterial skin infections.
- Sinusitis: Used for acute bacterial sinus infections.
Dosage and Administration
Levofloxacin is available in oral and intravenous forms. Dosage depends on the type and severity of the infection but is typically administered once daily. It’s crucial to follow the prescribed regimen to ensure effectiveness and reduce the risk of resistance. buy levofloxacin wholesale
Side Effects
While levofloxacin is generally well-tolerated, some common side effects may include:
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
- Headache
- Dizziness
More serious side effects, though rare, can include tendon rupture, nerve damage, and severe allergic reactions. Patients should be aware of these risks, especially if they have a history of tendon problems or are taking corticosteroids.
Precautions
Levofloxacin should be used with caution in certain populations, such as those with a history of seizures, liver disease, or those who are pregnant or breastfeeding. It’s important to discuss any medical history with a healthcare provider before starting treatment.
Conclusion
Levofloxacin is a potent antibiotic effective against a wide range of bacterial infections. Its convenient dosing and broad spectrum of activity make it a valuable tool in modern medicine. However, as with any antibiotic, it should be used responsibly to minimize the risk of resistance and side effects. If you have questions about levofloxacin or its appropriate use, consult your healthcare provider for tailored advice.