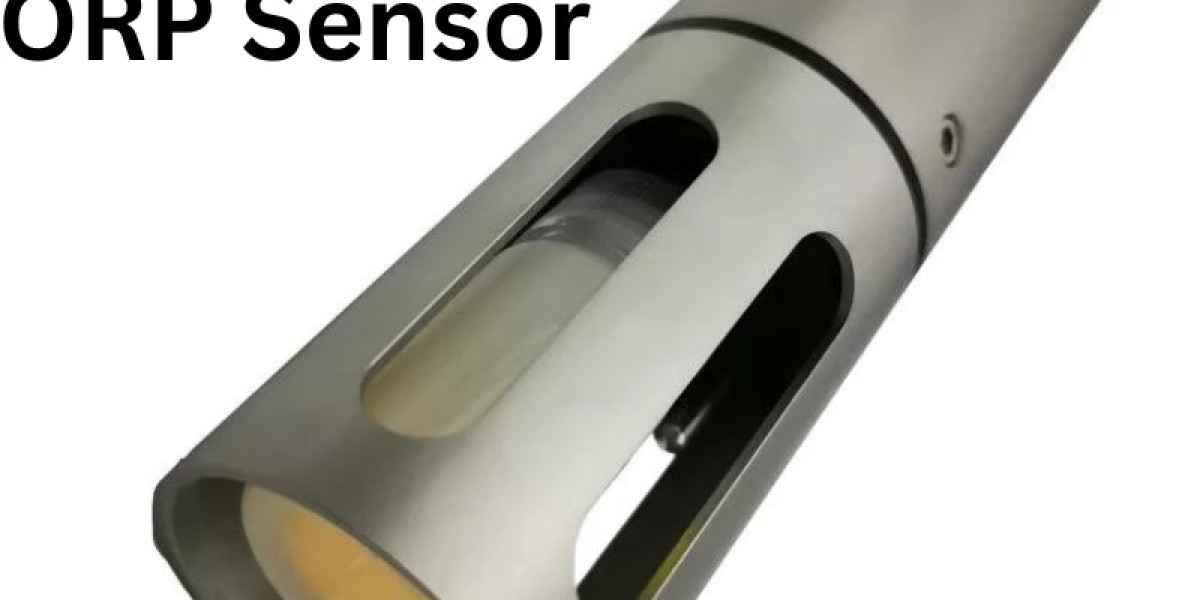
What is an ORP Sensor?
An ORP sensor measures the oxidation-reduction potential of a solution. In simpler terms, it tells us how much oxidizing or reducing agents are present in the water. This is crucial because the balance between these agents can significantly affect water quality. For example, high ORP values indicate a more oxidizing environment, which can help kill harmful bacteria and pathogens. Conversely, low ORP values suggest a reducing environment, which might lead to the growth of harmful organisms.
Why are ORP Sensors Important?
ORP sensors are widely used in many fields, including:
Water Treatment: In municipal water treatment plants, ORP sensors help ensure that water is safe for consumption. By maintaining the right balance of oxidizing agents, these sensors can prevent the growth of harmful bacteria and viruses.
Aquaculture: For fish farming, maintaining optimal water quality is essential. ORP sensors help monitor the health of aquatic environments, ensuring that fish live in clean, safe water.
Swimming Pools: Keeping pool water clean and safe is a top priority for pool owners. ORP sensors help monitor the effectiveness of disinfectants like chlorine, ensuring the water remains safe for swimmers.
Industrial Processes: Many industrial processes rely on specific chemical reactions that require precise control of oxidation and reduction reactions. ORP sensors provide real-time data to help maintain the right conditions for these processes.
How Do ORP Sensors Work?
ORP sensors consist of a probe that is placed in the water. This probe contains two electrodes: a reference electrode and a measuring electrode. When the probe is immersed in water, the electrodes measure the electrical potential difference between them, which is influenced by the oxidation and reduction reactions occurring in the solution. The sensor then converts this measurement into a digital ORP value, usually expressed in millivolts (mV).
Installing and Maintaining ORP Sensors
Installing an ORP sensor is relatively straightforward. Most sensors can be mounted directly in the water or connected to a flow cell. It's essential to ensure that the sensor is calibrated correctly to obtain accurate readings. Calibration typically involves comparing the sensor's readings to a known standard solution.
Maintenance is also crucial for accurate measurements. Regular cleaning and checking of the reference electrode are necessary to prevent fouling and ensure the sensor functions correctly. Depending on the specific model, you might need to replace the sensor every 1-2 years to maintain accuracy.
Conclusion
In summary, ORP sensors are invaluable tools for monitoring water quality across various applications. They help ensure that our water is safe for drinking, swimming, and supporting aquatic life. By understanding how these sensors work and their importance in maintaining water quality, you can appreciate the role they play in our daily lives. Whether you’re a pool owner, a fish farmer, or someone interested in water treatment, knowing about ORP sensors can help you make informed decisions about water safety and quality.